Understanding What is Video Rendering and Its Importance
Explore what is video rendering, why it matters, and how it works for creators, marketers, and filmmakers in this comprehensive guide.
Understanding What is Video Rendering and Its Importance
Video rendering shapes everything from viral ads to blockbuster movies and lets creators turn raw ideas into visual magic. Most people think of flashy effects or stunning graphics, but here is where it gets interesting. About 90 percent of modern visual storytelling would be impossible without rendering technologies that process millions of calculations per second. This is not just about putting pictures together. It is a hidden process that decides how stories are actually seen and felt.

Table of Contents
- Defining Video Rendering: What It Is And Its Purpose
- The Significance Of Video Rendering In Content Creation
- How Video Rendering Works: The Process Explained
- Key Concepts And Technologies Behind Video Rendering
Quick Summary
| Takeaway | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Video rendering transforms raw data into polished visuals | It converts various visual layers into a final product that tells stories and captures viewers' attention. |
| Rendering enhances emotional and brand messaging | Sophisticated rendering allows creators to convey complex messages clearly, giving emotional depth and brand consistency. |
| Powerful GPUs accelerate rendering processes | Modern rendering utilizes advanced graphics processing units to speed up calculations for higher quality visuals without high costs. |
| Color encoding is crucial in video rendering | Understanding color representation systems like RGB and HDR is essential for accurate visual output in rendering. |
| Rendering technology democratizes content creation | Advanced tools enable smaller teams and independent creators to produce high-quality visuals, enhancing diverse storytelling. |
Defining Video Rendering: What It Is and Its Purpose
Video rendering transforms raw digital video data into a final, polished visual product that communicates stories, messages, and experiences. At its core, rendering is a sophisticated computational process where video editing software converts multiple layers of visual information into a single, cohesive output that viewers can watch and enjoy.
The Technical Foundation of Video Rendering
Rendering represents a complex computational workflow where computer programs generate photorealistic or stylized images from digital models and sequences. According to computer graphics research, the process involves synthesizing images by processing geometric, textural, lighting, and shading information contained within scene files.
Key components involved in video rendering include:
- Geometric Data: The structural information defining shapes and objects
- Texture Mapping: Application of surface details and visual characteristics
- Lighting Simulation: Calculating how light interacts with different surfaces
- Shading Algorithms: Determining color, depth, and visual complexity
Purpose and Significance in Digital Media
Video rendering serves multiple critical functions across various industries. Professional video creators, filmmakers, game developers, and marketing teams rely on rendering to transform raw footage into polished, compelling visual narratives. The process enables advanced visual effects, smooth transitions, color grading, and the integration of complex graphical elements.
Rendering is not merely a technical step but a creative transformation. It takes disconnected visual elements and weaves them into a seamless, engaging experience that communicates ideas, evokes emotions, and captures audience attention. Whether producing a short social media clip or a full-length cinematic production, rendering turns conceptual ideas into tangible visual stories.
The computational complexity of rendering means that high-quality outputs require significant processing power. Modern rendering techniques leverage advanced graphics processing units (GPUs) and sophisticated software algorithms to generate increasingly realistic and intricate visual experiences in shorter timeframes.
The Significance of Video Rendering in Content Creation
Video rendering has revolutionized digital content creation, transforming how professionals and creators produce visual media across multiple industries. From marketing campaigns to cinematic experiences, rendering enables sophisticated storytelling techniques that were previously impossible or prohibitively expensive.
Enhancing Visual Communication and Brand Storytelling
According to digital media research, rendering provides creators unprecedented control over visual narrative elements. Marketing teams and content producers can now craft precise visual experiences that communicate complex messages with remarkable clarity and emotional resonance.
Key advantages of advanced rendering in content creation include:
- Emotional Impact: Creating visually stunning experiences that connect with audiences
- Brand Consistency: Maintaining uniform visual quality across different media platforms
- Creative Flexibility: Enabling complex visual effects and storytelling techniques
Technical Capabilities and Creative Potential
Modern rendering technologies empower creators to transcend traditional production limitations. Professionals can now generate photorealistic environments, simulate complex lighting scenarios, and integrate computer generated imagery seamlessly with live action footage. This technological advancement allows for unprecedented creative expression across film, advertising, gaming, and digital media.
The computational power required for high quality rendering means that creators can produce cinema quality visuals without massive production budgets. Small teams and independent creators now have access to tools that were once exclusive to major studios. These technological democratization enables more diverse voices to share compelling visual stories.

Rendering has become an essential bridge between imagination and visual reality. By transforming raw digital information into polished, meaningful content, rendering technologies continue to expand the boundaries of creative expression and storytelling in the digital age.
How Video Rendering Works: The Process Explained
Video rendering is a sophisticated computational process that transforms complex digital information into smooth, visually compelling sequences. By converting raw digital data into polished visual experiences, rendering acts as a critical bridge between digital design and final visual output.
The Technical Mechanics of Rendering
According to computer graphics research, rendering involves converting virtual 3D scenes into 2D images by determining the color and characteristics of each pixel. This intricate process requires multiple computational steps that analyze and synthesize visual elements with remarkable precision.
The core stages of video rendering include:
- Scene Preparation: Organizing digital assets and defining spatial relationships
- Geometry Processing: Calculating object shapes and surface interactions
- Lighting Simulation: Determining how light reflects and interacts with surfaces
- Pixel Calculation: Generating final color and texture for each screen element
To help clarify the multi-step workflow of video rendering, the following table summarizes the main technical stages involved in the process and what each stage accomplishes.
| Rendering Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Scene Preparation | Organizes digital assets and defines the spatial relationships between objects and elements. |
| Geometry Processing | Calculates object shapes, surface interactions, and spatial transformations. |
| Lighting Simulation | Determines how light reflects, refracts, and interacts with all surfaces in the scene. |
| Pixel Calculation | Generates the final color, depth, and texture details for each element displayed on screen. |
Computational Strategies and Optimization
Modern rendering techniques employ advanced algorithms and powerful graphics processing units (GPUs) to accelerate visual computations. These strategies allow for increasingly complex visual representations, enabling creators to generate photorealistic environments and intricate visual effects with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
The rendering process involves transforming mathematical models into visual experiences. Each frame requires complex calculations that assess geometric transformations, lighting conditions, texture mapping, and color representation. By breaking down these computational tasks into systematic workflows, rendering technologies can generate increasingly sophisticated visual narratives.
As computational technologies advance, rendering continues to push the boundaries of visual storytelling. From creating immersive cinematic experiences to generating real time graphics in video games, rendering represents a critical intersection of technological innovation and creative expression.
Key Concepts and Technologies Behind Video Rendering
Video rendering represents a complex ecosystem of technological innovations that transform digital information into visually compelling experiences. Understanding the fundamental technologies and concepts driving this process reveals the intricate mechanisms that enable modern digital storytelling.
Color Encoding and Image Processing
According to digital media technologies research, color representation forms the foundational framework of video rendering. Modern rendering technologies utilize sophisticated color encoding systems that translate digital data into precise visual representations.
Critical color encoding technologies include:
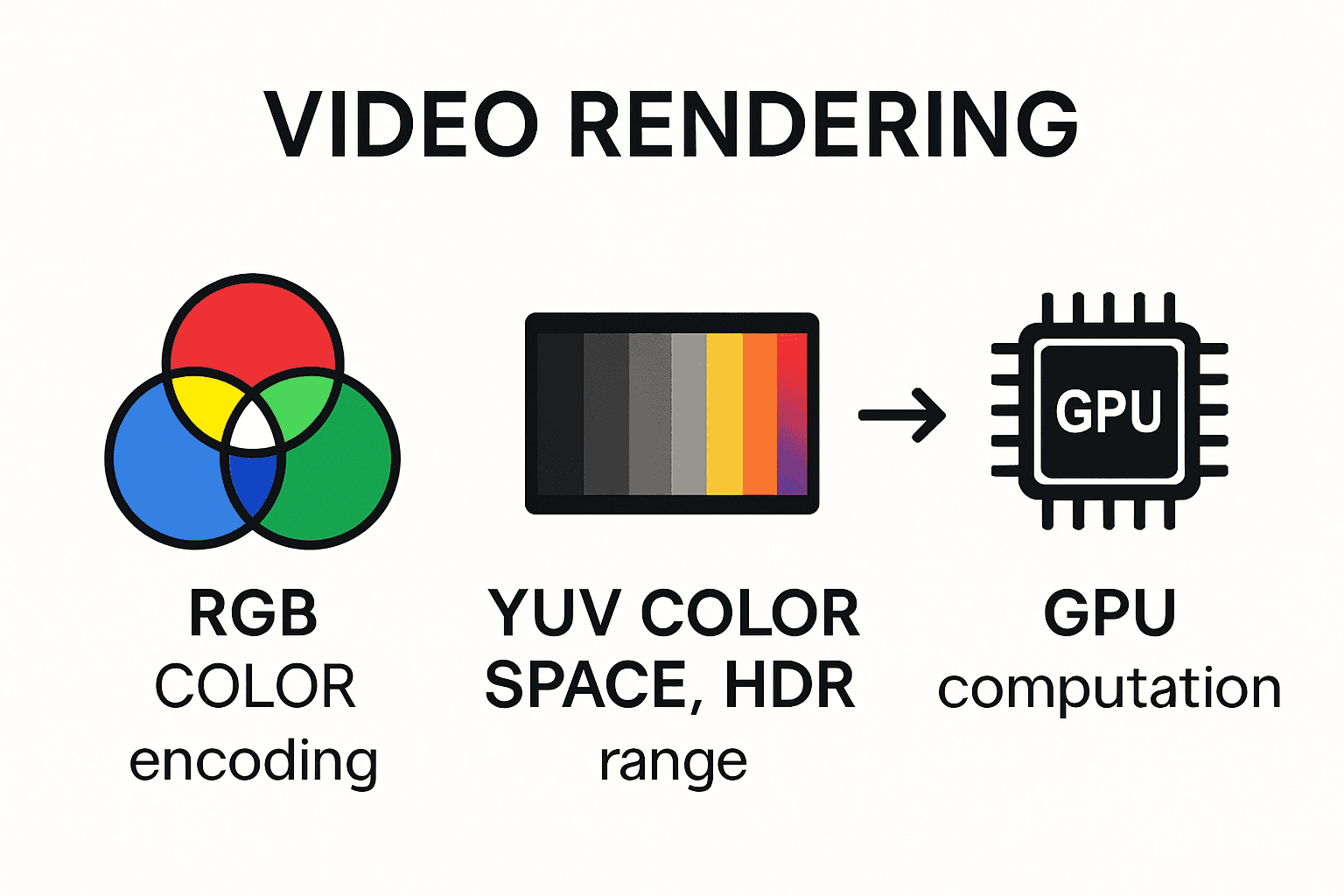
- RGB Color Model: Representing colors through red, green, and blue intensity values
- YUV Color Space: Separating luminance and chrominance for efficient video compression
- High Dynamic Range (HDR): Enabling broader color ranges and enhanced visual depth
Computational Rendering Architectures
Advanced rendering technologies leverage complex computational strategies to generate high quality visual outputs. Graphics processing units (GPUs) have revolutionized rendering capabilities by providing massive parallel processing power that can handle intricate visual calculations simultaneously.
The computational architecture of modern rendering involves multiple sophisticated processes that work in concert. These include geometric transformation algorithms, ray tracing techniques, and advanced texture mapping technologies that can generate increasingly photorealistic visual experiences.
As computational technologies continue to evolve, rendering techniques become more nuanced and powerful. From creating immersive cinematic environments to generating real time graphics in interactive media, rendering technologies represent a critical intersection of mathematical precision and creative expression.
Transform Your Ideas Into Cinematic Videos—No Rendering Experience Needed
Are you struggling with the complex and time-consuming world of video rendering described in the article above? Many creators face roadblocks due to the technical demands of scene management, lighting simulations, and color encoding when all they want is to tell a compelling story visually. If your goal is high-quality output but you lack the time or expertise to master rendering workflows, you are not alone. The process is daunting—but it no longer needs to be your challenge.
Experience how easy professional video creation can be with Palmedor.ai. Let our AI-powered platform handle the rendering, scene creation, and editing for you. Describe your concept or upload images, and watch your ideas become polished, ready-to-share videos. Now is the perfect moment to explore how simple video production can be. Visit Palmedor.ai today and transform your next project with just a few clicks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is video rendering?
Video rendering is the process of transforming raw digital video data into a final, polished visual product that conveys stories and messages through intricate computational workflows.
Why is video rendering important in content creation?
Video rendering is crucial because it enhances visual communication, allowing creators to produce polished, engaging narratives and maintain brand consistency across different media platforms.
What are the key components of video rendering?
The main components of video rendering include geometric data, texture mapping, lighting simulation, and shading algorithms, which work together to create visually compelling outputs.
To enhance understanding of the key components underlying video rendering, the table below defines each component and its main function within the rendering process.
| Component | Definition |
|---|---|
| Geometric Data | Information defining the shapes, positions, and structure of visual objects. |
| Texture Mapping | Application of detailed surface patterns and visual characteristics to objects. |
| Lighting Simulation | Computational modeling of how light interacts with and illuminates scene elements. |
| Shading Algorithms | Techniques that determine color, depth, and the overall appearance of visuals. |
How does video rendering work?
Video rendering involves multiple stages, including scene preparation, geometry processing, lighting simulation, and pixel calculation, utilizing advanced algorithms and graphics processing units (GPUs) to produce high-quality visuals.