Understanding Sound Design Fundamentals for Creators
Explore sound design fundamentals for creators. Learn its importance, concepts, and how it shapes multimedia experiences.
Understanding Sound Design Fundamentals for Creators

Sound design is everywhere, shaping the way you feel during movies, games, and even everyday ads. You might think it is just about adding cool effects or background noise, but that barely scratches the surface. The surprise is that sound design can literally change how your brain processes emotion and attention—one study found measurable emotional changes in both kids and adults from simple shifts in sound and space. This is why the true power of sound design lies in its ability to tell stories without a single word.
Table of Contents
- What Is Sound Design And Its Importance?
- Key Elements Of Sound Design And Their Roles
- The Relationship Between Sound And Emotion In Media
- How Sound Design Enhances Storytelling
- Real-World Applications Of Sound Design Fundamentals
Quick Summary
| Takeaway | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Sound design is a creative discipline. | It transforms raw audio into rich, immersive experiences that enhance narrative and emotional engagement across various media. |
| Key elements include clarity and ambiance. | Mixing dialogue, sound effects, and music strategically ensures audio communicates mood and context effectively. |
| Sound triggers emotional responses. | By manipulating frequency and rhythm, sound designers can evoke specific feelings in the audience, enhancing the storytelling experience. |
| Sound design is crucial for narrative depth. | It adds emotional nuance and context, making stories more engaging and helping audiences understand complex narratives. |
| Applications extend beyond traditional media. | Modern sound design techniques enhance experiences in areas like virtual reality, gaming, and automotive engineering. |
What is Sound Design and Its Importance?
Sound design represents a sophisticated creative discipline that transforms raw audio into compelling sensory experiences across multiple media platforms. At its core, sound design is the strategic art of creating, selecting, and manipulating audio elements to enhance narrative, emotional impact, and audience engagement.
The Fundamental Definition
Sound design goes beyond simple audio recording. It involves crafting intricate soundscapes that communicate mood, context, and psychological nuance. Professionals in this field carefully blend dialogue, sound effects, ambient noise, and musical compositions to construct immersive auditory environments that complement visual storytelling.
According to Moving Image Studio, sound design serves as a critical communication tool that transmits information while simultaneously creating specific atmospheric qualities. This means sound designers are not just technicians but creative storytellers who use audio as their primary narrative language.
Key Elements of Sound Design
Sound design encompasses several crucial components that work together to create meaningful audio experiences:
- Dialogue Clarity: Ensuring spoken words are crisp, intelligible, and emotionally resonant
- Sound Effect Construction: Creating or sourcing authentic audio representations of physical actions and environments
- Musical Integration: Strategically using musical elements to underscore emotional states and narrative progression
- Spatial Audio Manipulation: Designing sound that creates a sense of depth, movement, and dimensionality
Professional sound designers understand that every audio element serves a specific purpose. Whether designing for film, video games, advertising, or digital media, their goal remains consistent: to create audio experiences that feel authentic, engaging, and emotionally powerful.
By meticulously layering and balancing different sound components, designers transform simple audio into rich, multilayered narratives that captivate audiences and enhance overall storytelling effectiveness.
Key Elements of Sound Design and Their Roles
Sound design is a complex art form that requires mastering several interconnected technical and creative elements. Understanding these components allows creators to build rich, immersive auditory experiences that communicate narrative depth and emotional resonance.
Foundational Sound Components
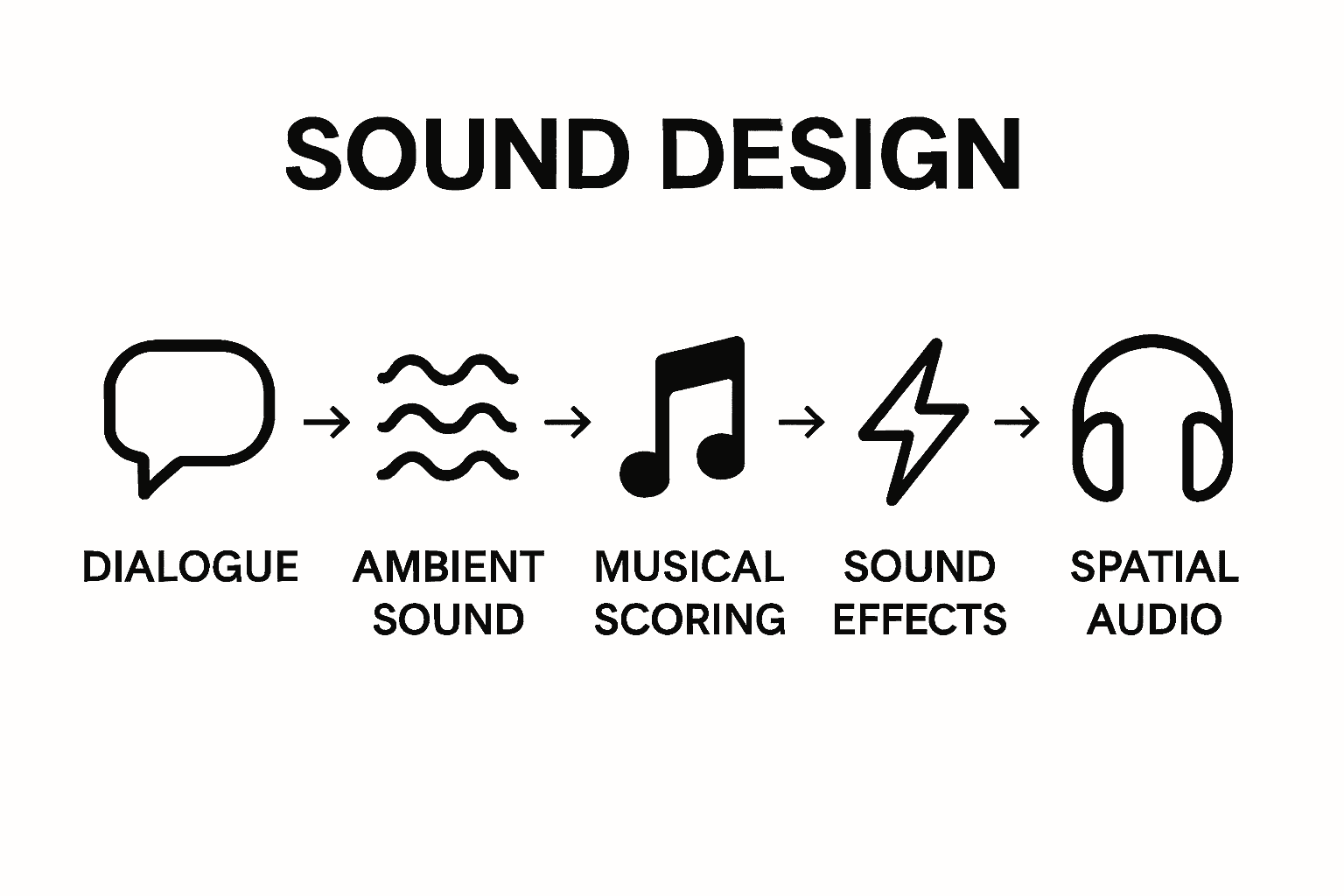
Sound design is built upon multiple fundamental elements that work synergistically to create meaningful audio landscapes. According to University of Silicon Valley, these core components include dialogue clarity, ambient sounds, musical scoring, sound effects, and spatial audio mixing.
Technical and Creative Dimensions
Each sound design element serves a unique purpose in constructing audiovisual narratives:
- Dialogue Clarity: Ensures spoken words are crisp, intelligible, and emotionally nuanced
- Ambient Sound Layering: Creates environmental context and psychological atmosphere
- Musical Integration: Provides emotional subtext and narrative progression
- Sound Effect Synchronization: Adds authenticity and sensory depth to visual experiences
Professional sound designers understand that these elements are not isolated techniques but interconnected components of a holistic auditory experience.
To help clarify the primary components and their functions, the table below summarizes the foundational elements of sound design and the role each plays in media production.
| Sound Design Element | Function/Role |
|---|---|
| Dialogue Clarity | Ensures spoken words are crisp, intelligible, and carry appropriate emotional nuance |
| Ambient Sound Layering | Establishes environmental context and psychological atmosphere |
| Musical Integration | Provides emotional subtext and supports narrative progression |
| Sound Effect Synchronization | Adds authenticity and sensory depth by aligning audio cues with visual actions |
| Spatial Audio Mixing | Creates the perception of depth, movement, and immersive dimensionality within the soundscape |
For instance, adjusting a sound's frequency can dramatically alter its perceived emotional quality. Low frequencies might communicate tension or mystery, while higher frequencies can suggest excitement or anxiety. Similarly, spatial audio mixing allows designers to guide audience attention and create immersive three-dimensional soundscapes.
The art of sound design transcends technical proficiency. It requires an intuitive understanding of how audio elements interact to create meaningful sensory experiences that complement visual storytelling and enhance audience engagement.
The Relationship Between Sound and Emotion in Media
Sound possesses a profound psychological power to trigger, modulate, and intensify human emotional experiences. In media production, sound design serves as a sophisticated emotional architecture that communicates complex feelings through strategic audio manipulation.
Neurological Foundations of Audio Emotional Response
Sound interacts with our brain in nuanced ways that transcend simple auditory perception. When exposed to specific sound frequencies, timbres, and rhythmic patterns, our neurological systems activate emotional processing centers, generating immediate psychological and physiological responses.
According to Pubmed Research, children and adults demonstrate measurable emotional variations when experiencing arousing sounds and spatially complex audio treatments. This suggests that sound design is not merely decorative but a powerful communication mechanism that directly influences audience emotional states.
This table outlines how specific audio techniques within sound design contribute to eliciting particular emotions, providing insight into the psychological impact of different sound manipulation strategies.
| Technique | Description | Emotional Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Modulation | Adjusting pitch and range of sounds | Low: tension/melancholy; High: excitement/anxiety |
| Rhythmic Complexity | Varying rhythm and beat structure | Irregular: uncertainty/excitement |
| Tonal Variation | Changing tone quality (sharpness, smoothness) | Sharp: danger; Smooth: comfort |
| Spatial Dynamics | Using 3D placement and movement within audio | Immersion; heightens emotional realism |
Emotional Dimensions of Sound Design
Sound designers leverage several key techniques to evoke emotional responses:
- Frequency Modulation: Lower frequencies typically communicate tension or melancholy
- Rhythmic Complexity: Irregular rhythms can generate feelings of uncertainty or excitement
- Tonal Variation: Sharp tones often signify danger, while smooth tones suggest comfort
- Spatial Dynamics: Three-dimensional sound placement creates immersive emotional landscapes
These techniques work together to construct sophisticated emotional narratives. A suspenseful film scene might utilize low-frequency rumbles, erratic percussion, and strategically placed sound effects to generate audience anxiety. Conversely, a tender moment could employ soft, harmonious tones that create a sense of intimacy and emotional vulnerability.
Understanding sound's emotional mechanics allows media creators to craft experiences that resonate deeply with audiences. By treating sound as an emotional language rather than mere background noise, designers can transform passive viewers into actively engaged participants in the narrative journey.
How Sound Design Enhances Storytelling
Storytelling transcends visual narrative, with sound design serving as a powerful narrative instrument that communicates subtext, emotion, and psychological complexity beyond what images alone can achieve. Sound transforms linear storytelling into multidimensional experiences that engage audiences on deeper sensory and emotional levels.
Narrative Depth Through Audio
Sound design operates as an invisible storyteller, providing critical context and emotional nuance that enriches narrative comprehension. Each audio element functions like a linguistic component, contributing meaningful information that guides audience interpretation and engagement.
According to Digital Media Arts, sound can evoke emotions, establish settings, develop character perspectives, and advance plot progression through strategic audio manipulation.
Storytelling Dimensions of Sound
Sound designers leverage multiple techniques to enhance narrative communication:
- Contextual Atmosphere: Creating environmental soundscapes that reveal location, time period, and psychological mood
- Emotional Subtext: Using audio dynamics to communicate unspoken character emotions
- Narrative Pacing: Manipulating sound rhythm to control story tension and audience anticipation
- Character Development: Utilizing unique sound signatures to represent individual character traits
In practice, these techniques transform storytelling from passive observation to active participation. A character walking through a forest might have subtly different footstep sounds depending on their emotional state subtle rustling suggesting anxiety, confident steps indicating determination. Background ambient sounds can communicate unspoken narrative information, such as distant industrial noises hinting at urban decay or gentle wind sounds suggesting pastoral tranquility.
The art of sound design lies in its ability to communicate complex narratives through auditory experiences. By treating sound as a language unto itself, creators can craft stories that resonate far beyond visual representation, inviting audiences into immersive emotional landscapes that transcend traditional storytelling boundaries.
Real-World Applications of Sound Design Fundamentals
Sound design fundamentals extend far beyond traditional media production, finding innovative applications across numerous industries and technological domains. These principles enable professionals to create immersive, meaningful auditory experiences that enhance user interaction and perception.
Technological Innovation in Sound Design
Modern sound design has evolved from a purely creative discipline to a critical technological interface that bridges human perception and digital experiences. Professionals now leverage sophisticated techniques to generate context-aware audio environments that adapt dynamically to user interactions.
According to Augmented Reality Research, emerging technologies are developing systems capable of generating real-time, material-specific sounds by analyzing physical object characteristics through advanced computer vision techniques.
Interdisciplinary Sound Design Applications
Sound design fundamentals find expression across multiple professional domains:
- Virtual Reality: Creating immersive spatial audio experiences
- Video Game Development: Generating responsive, dynamic soundscapes
- Medical Training: Simulating realistic procedural audio environments
- Architectural Acoustics: Designing spatial sound experiences in physical spaces
- Automotive Engineering: Developing sophisticated in-vehicle sound experiences
In practice, these applications demonstrate sound design's transformative potential. For instance, automotive engineers now use precise sound manipulation to create specific emotional responses through carefully engineered engine sounds. Video game developers employ advanced sound design to generate adaptive audio landscapes that respond to player actions in real time.
The intersection of sound design with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning promises even more sophisticated audio experiences. By treating sound as a dynamic, responsive medium, professionals can create increasingly nuanced and contextually intelligent auditory interactions that transcend traditional sensory boundaries.

Transform Sound Design Fundamentals into Cinematic Video Creation
Have you mastered the essential elements of sound design but struggle to bring those concepts into engaging, professional-grade video content? Many creators know the importance of dialogue clarity, spatial audio, and emotional storytelling through sound. Yet, translating these fundamental skills into fully realized videos can feel overwhelming, especially if you lack expert technical tools or production support.
With Palmedor.ai, you can finally bridge the gap from conceptual understanding to finished creation. Our AI-powered platform allows you to craft cinematic videos with compelling soundscapes right from your ideas, scripts, or images. Whether you are aiming for brand storytelling or social media clips, simply describe your vision and let our intelligent system handle editing, scene creation, and professional sound integration. Want to see how easy it is to unlock the potential of your sound design knowledge in video? Explore our powerful features and get started on Palmedor.ai today. Empower your creativity and produce videos that truly resonate—now is the perfect moment to turn your expertise into real results.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is sound design?
Sound design is the creative process of creating, selecting, and manipulating audio elements to enhance narrative, emotional impact, and audience engagement in various media.
How does sound design impact storytelling?
Sound design enhances storytelling by providing emotional subtext, establishing atmosphere, and developing character perspectives through carefully crafted audio elements.
What are the key components of sound design?
The key components of sound design include dialogue clarity, ambient sounds, musical scoring, sound effects, and spatial audio mixing—all working together to create immersive auditory experiences.
How does sound design evoke emotional responses?
Sound design evokes emotional responses by manipulating elements such as frequency, rhythm, tonal variation, and spatial dynamics, thus triggering specific psychological reactions in the audience.